
Confidentiality is the security principle that controls access to information. It is designed to ensure the wrong people cannot gain access to sensitive information while ensuring the right people can access it.
Access to information must be restricted only to those who are authorized to view the required data. Data can be categorized according to the type and severity of damage that could happen to it should it fall into unauthorized hands. According to these categories, strict measures can then be implemented.
Protecting confidentiality may also include special training for those who share sensitive data, including familiarizing authorized users with security risk factors and teaching them how to guard vulnerable data assets.
In addition to training, strong passwords and password-related best practices must be used as well as information about social engineering attacks to prevent them from unwittingly avoiding proper data-handling rules and potentially causing disastrous results.
An example of a method used to ensure confidentiality is the use of data encryption. Two-factor authentication is now becoming the norm for authenticating users to access sensitive data, while user IDs and passwords should be considered standard practice.
Other methods include biometric verification, security tokens, and digital certificates. Users should also be cautious to reduce the number of places where the information appears and where sensitive data is transmitted in order to complete a transaction.
The second component of the triad, integrity assures the sensitive data is trustworthy and accurate. Consistency, accuracy, and trustworthiness of data should be maintained over its life cycle. Sensitive data should not be altered in transit, and security measures, such as file permissions and user access controls, should be taken to make sure that it cannot be modified by unauthorized users.
In addition, version control should be used to prevent unintentional changes and deletions from authorized users from becoming a problem. Other measures should also be taken to detect data changes that might occur due to a non-human-caused event, such as a server crash or an environmental failure. Sensitive data should also include cryptographic checksums for verification of integrity. In addition, backups or redundancy plans should be planned and implemented to restore any affected data in case of an integrity failure or security breach in order to restore data back to its correct state.
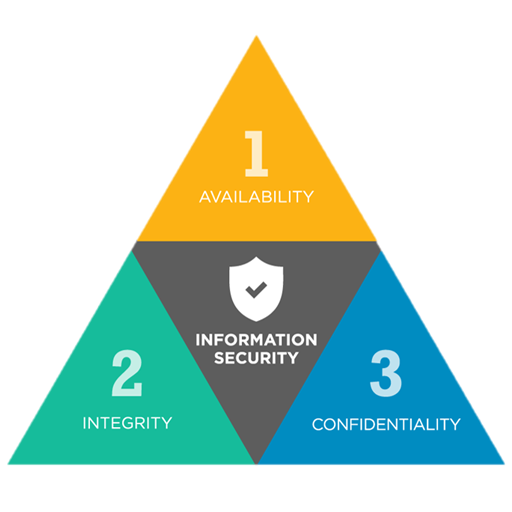
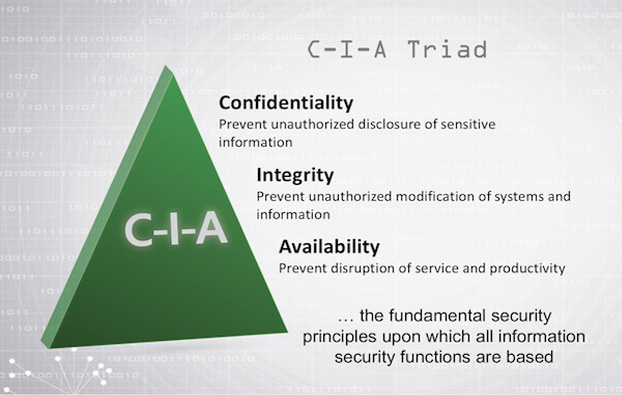
Availability is the guarantee of reliable and constant access to your sensitive data by authorized people. It is best guaranteed by properly maintaining all hardware and software necessary to ensure the availability of sensitive data. It’s also important to keep up with system upgrades. Providing adequate communication throughput and preventing bottleneck helps as well. Redundancy, failover, RAID, and clustering are important measures that should be considered to avoid serious availability problems.
A quick, adaptive disaster recovery plan is crucial for the worst-case scenarios, which will depend on the successful execution of a full disaster recovery plan.
Safeguards against interruptions in connections and data loss should consider unpredictable events such as a fire or a natural disaster. To prevent data loss, a backup should be located in a geographically separate location, and in a fireproof, waterproof vault.
To prevent downtime due to malicious attacks such as denial-of-service DOS attacks and network intrusions, extra software and security equipment should be used as well.


neiplynup
2022-10-26 23:57
Although noted as being a selective pro drug stromectol singapore